01
Accelerating Globalization: Sales, Production and Procurement
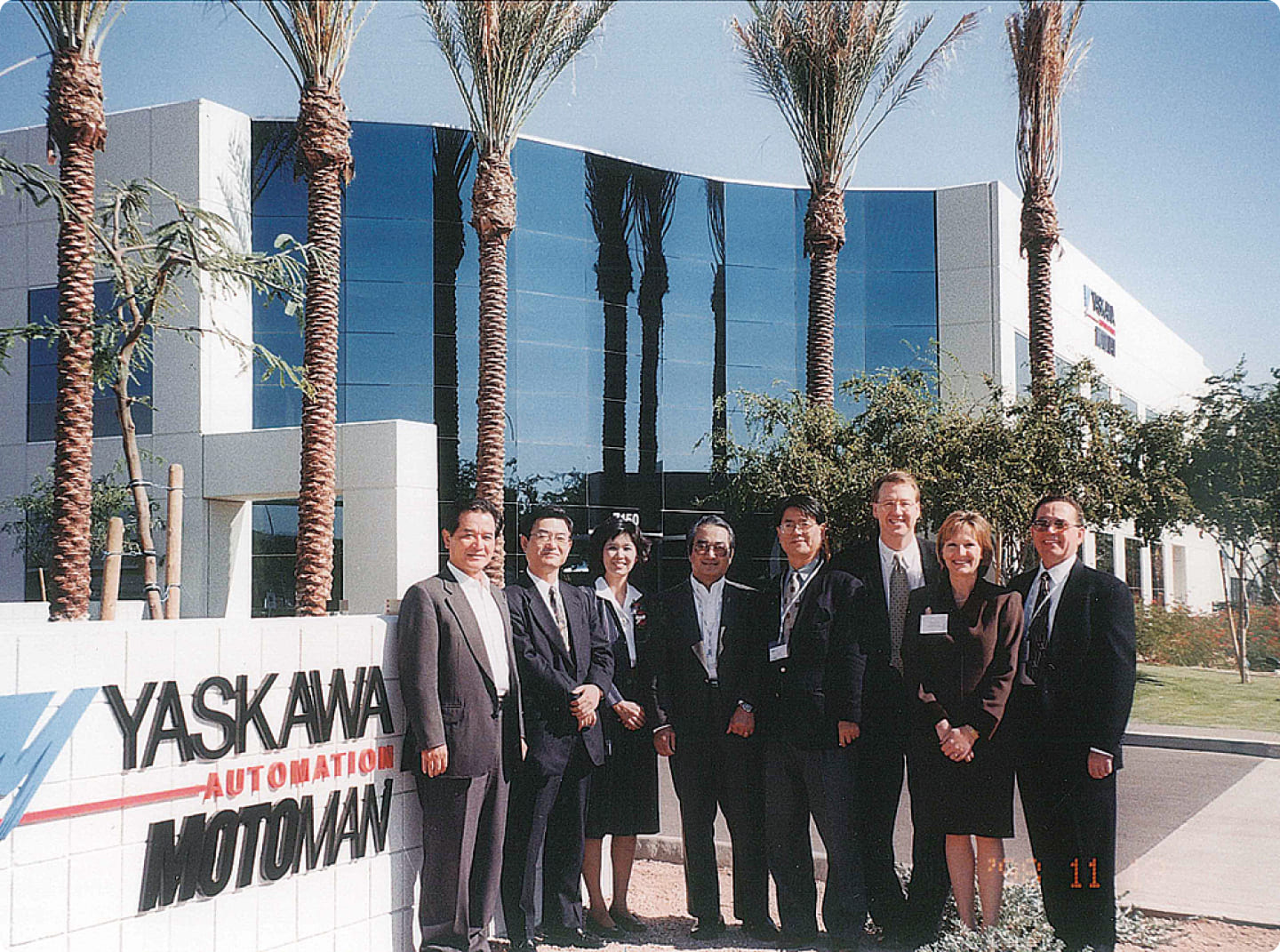
In 1967, the company founded Yaskawa America in the U.S. with the aim of expanding sales of its mainstay products such as Minertia Motors.
Beginning with that, we accelerated globalization in the 1960s by expanding our overseas sales network, establishing a global production structure based on in-demand production, and developing a global procurement network. Today, we operate out of business sites in 30 countries and 29 production sites in 13 countries.
Expansion of Overseas Sales Network
Servo motors and inverters / AC Drives were in demand in the U.S. for automobiles, pumps, and semiconductors, in South Korea for automobiles, electronics, steel, and shipbuilding, and in Asia for port cranes, heavy electric power plants, etc., in line with the industrial growth of each country. In addition, we expanded our sales network by establishing local companies to link to large orders, mainly for mainstay products.
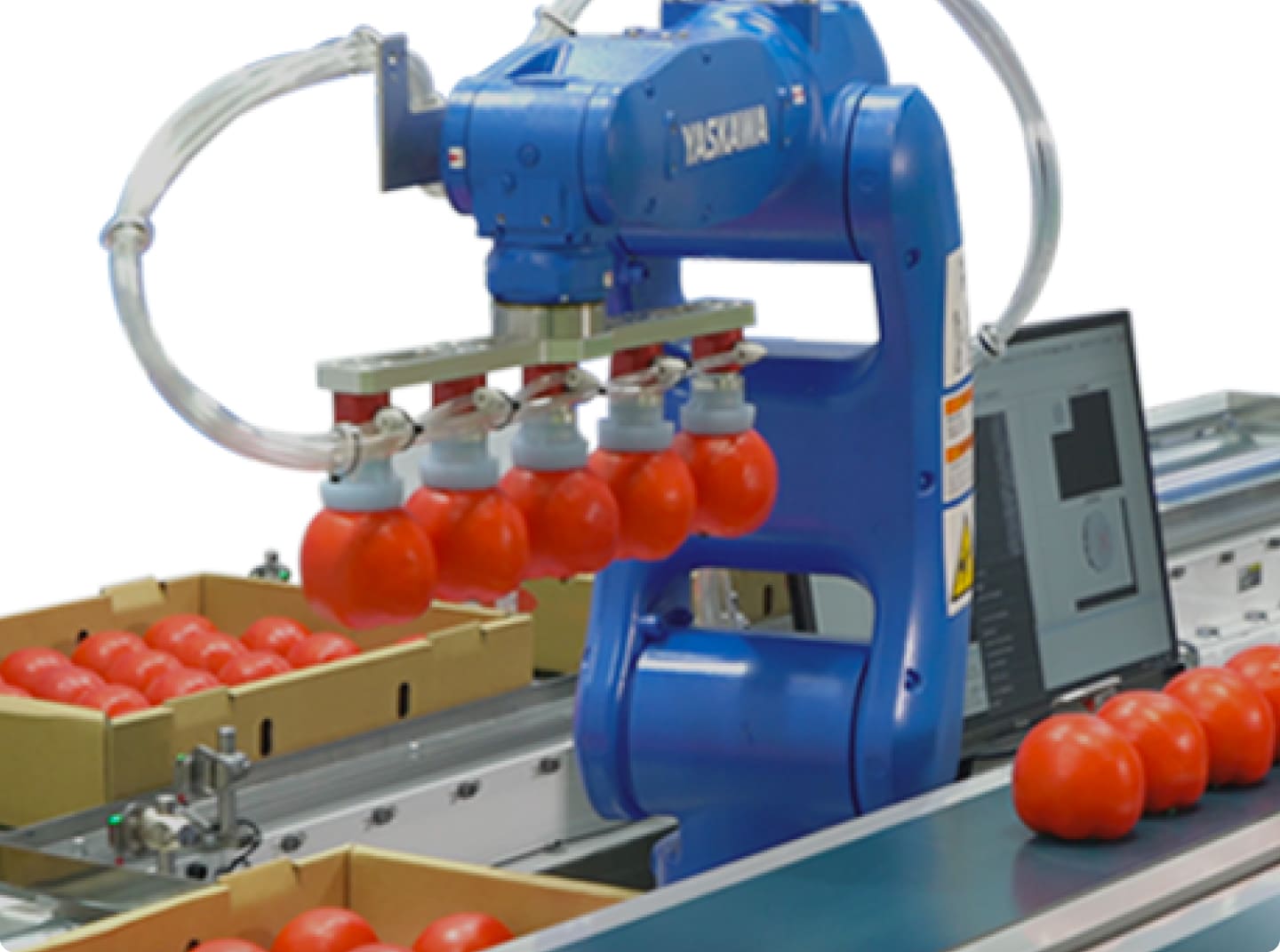
In terms of robotics, we have established a global sales network mainly since the 1990s through M&A of local SIers in Europe and the U.S., and joint ventures with local manufacturers in China.
Establishment of Global Production Structure
In terms of global production, based on the concept of in-demand production, we have developed a production structure in areas where customer is in demand, such as in Europe, the U.S., and elsewhere. We began producing inverters /AC Drives and robots in the 1990s, and servo motors / AC Amplifiers in China in the 2000s, paving a way forward to increase our market share in response to regional needs.
Development of Global Procurement Network
Global procurement began with consideration of overseas procurement in search of cost benefits from the appreciation of the Japanese YEN in the 1990s. As Japanese parts manufacturers gradually expanded into China, overseas procurement rates increased from print boards to cast and machinery parts. In the 2000s, along with the expansion of global production that we advanced, we expanded to local procurement by each base, especially in China, and global procurement and production became full-scale.
Outline of international expansion
- 1967
- Yaskawa America founded
- 1980
- Yaskawa Europe founded
- 1991
- Yaskawa Singapore founded
- 1992
- Production of inverters began in the U.S.
- 1993
- Production of inverters began in Scotland
- 1994
- Shanghai office opened / Yaskawa Korea founded
Yaskawa America acquires 100% subsidiary MOTOMAN Corp for sales of robots
- 1995
- Yaskawa Singapore began an IPO (International Procurement Base) business
Beijing Office opened
Yaskawa China -Shanghai founded (Inverter production started in 1997)
- 1996
- Yaskawa China- Motoman limited founded (Robot production started in 1997)
- 1999
- Yaskawa Electric (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. founded
- 2008
- Yaskawa Electric (Shenyang) Co., Ltd. founded (Servo motors and amplifiers production started in 2010).
- 2018
- Robot production began in Slovenia
 Region
Region



 Principles & vision
Principles & vision
 Procurement
Procurement
 Sustainability for the Yaskawa Group
Sustainability for the Yaskawa Group
 Customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction
 Supply chain
Supply chain
 Social contribution
Social contribution
 Compliance & risk management
Compliance & risk management