Arc welding
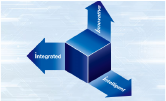
Arc welding is one of a major welding method where an arc is generated by electric discharge between the metal to be joined and the electrode (welding wire, etc.) of a welding torch equipped to the tip of the robotic arm, and the metal is melted and joined by the heat. It is widely used for joining metals together. In order to stabilize the arc and protect the molten metal from the atmosphere, welding methods such as MIG welding, MAG welding, CO 2 welding, TIG welding, and plasma welding are selected depending on the type of gas used and whether the electrodes are consumed.
Welding torches are lightweight and use industrial robots that are smaller than spot welding. In arc welding, molten metal called spatter scatters, and this unintentionally damages the metal surface, so reducing the amount of spatter is an issue from the viewpoint of quality improvement. Yaskawa has developed and provides the EAGL method which can reduce this sputtering to the utmost limit.

Spot welding
Spot welding is a method in which two pieces of metal to be joined are sandwiched by the strong force of a gun which is called spot gun, and then welded with resistance heat generated by passing a large current from the gun to the sandwiched part. It is used for joining relatively thin metals and widely used for welding automotive bodies. Because the spot gun is large and heavy, usually a robot with a large payload capacity compared to arc welding is adopted. Spot welds can include laser spot welds and seam welds with rolled electrodes, but simply spot welds usually refer to welds using spot guns.
In spot welding, due to the continuous short pitches as well as the heaviness of spot gun, how to move the body arm smoothly and at high speed without vibration is important for shortening the tact time, which is the process work time. Yaskawa has developed and implemented a motion control technology for robotic applications for spot welding to reduce this vibration.
Handling
Handling is one of the application of gripping and carrying a workpiece* by a robotic hand attached to the tip of the robotic arm. A various type of models, from small to large, are manufactured to meet the customer‘sneeds. In addition, since the work to be handled ranges from machine parts to food, depending on the work, there are variations such as a work with a dust-proof and drip-proof robotic structure, a surface treatment that takes food into consideration, and a work using grease that is harmless even if put into mouth.
In addition, when the position of the workpiece is stacked randomly, the position of the object can be detected using a 2D or 3D vision sensor, etc., and when grasping the workpiece flowing on the conveyor, the conveyor synchronization function can be used.
*workpieces: Products or parts to work with the robot

Assembly
Robotic assembly is the application of attaching a handled part to another part. If you are installing the part with screws or bolts, install and screw in a special device called a nut runner to screw the robotic arm. When the position of the object to be assembled or the position of the parts is stacked randomly, various sensors are used, such as a vision sensor that detects the position with a camera to correct the deviation, and a “stroke” using a robotic force sensor when precise fitting is required.

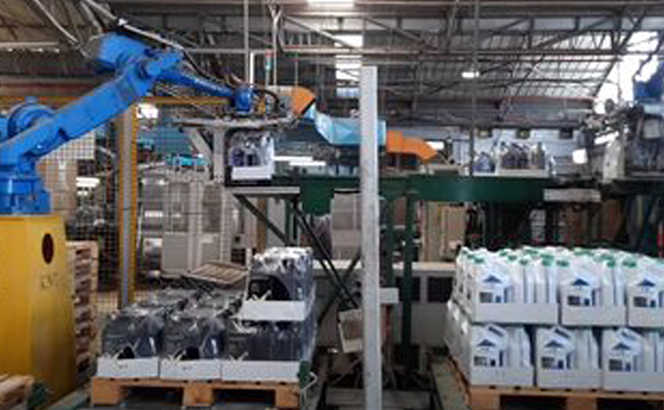
Palletizing
Palletizing is an application in which workpieces are piled up on transport pallets, which are often used for handling, especially when taking in or out a factory. There are various types of workpieces, such as cardboard boxes and bags, depending on the customer’s product and packaging style, and it is necessary to prepare a suitable hand for each type. In general, it is not necessary to swing up the workpiece, however, since the range of motion requires a wide range and a high height, a specially designed model with a small number of motors incorporated in the robotic structure is available.
On the other hand, there is also loading and unloading of the pallet, which is called depalletizing. For palletizing robots, the speed of motion control is important because of the repetition of simple movements.

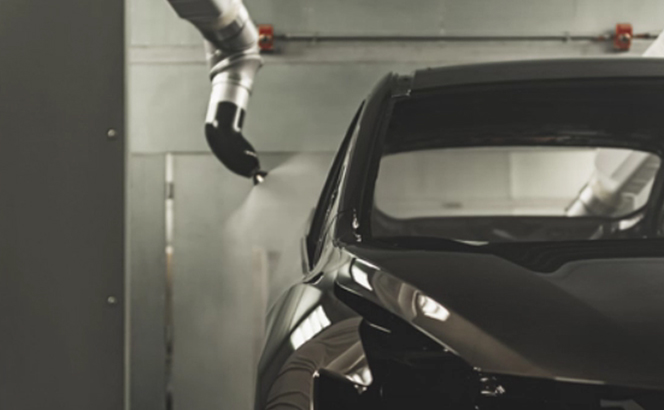
Paint
Paint is sprayed onto the work with a spray gun attached to the wrist. We have a wide range of products from small products to automobile and train body paints. In general, the spray paint is flammable, and in order to prevent fire in the event of an emergency, a special robotic structure is required that always supplies fresh air inside the robot and prevents flammable gases from entering.

Collaborative robot
Many industrial robots have been separated by means of safety fences, etc., to ensure the safety for workers, but collaborative robot is a breakthrough robot in regards to the safety measures that allow it to operate in the same space as workers. On the operation side, it has a direct teaching function that sets the path /trajectory by holding the robotic arm directly so that even those who have never operated the robot can operate it intuitively. Also, in terms of design, various ideas have been devised, such as the use of many curves, the design that does not pinch the fingers, and the incorporation of sensors to stop safely even if a person comes into contact with them. They are mainly used for handling and assembly, but recently they are being used in industries where industrial robots have not been introduced at a fast pace, such as the food industry.

Biomedical
Biomedical robot is applied to biomedical and medical applications such as bacteria testing and drug preparation. Because the robot works in place of a human, there is no danger of workers coming into contact with germs or chemicals, which helps improve the work environment. In addition, since there is no human error in the formulation of chemicals as in the past, stable work is realized and work can be continued even at night, contributing to improved production efficiency. Since the robot in this application is required to maintain a clean environment, it has a robotic structure that does not generate even tiny dust, and a structure that can be used for wiping and cleaning.

FPD (Flat Panel Display)/transporting glass substrates for solar cells
FPD (Flat Panel Display) and glass substrate transport for solar cells are applications for transporting thin glass substrates with a thickness of several millimeters, which are used for FPD such as liquid crystal and organic EL and solar cell panels. It transports large and flexible thin glass substrates at high speed. Since the glass substrates are set in layers at intervals of several tens of mm, a hand must be inserted into the gap at high speed to scoop up the glass substrates. In addition to requiring operation that takes into account the deflection of the glass substrate, it is also used in clean rooms, so it is designed to prevent from dust.

Semiconductor wafer conveyance
Semiconductor wafer transport application are usually incorporated into semiconductor manufacturing equipment manufactured by customers. Because silicon wafers are fragile and are transported at high speeds in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, high-speed and low-vibration operation is required. In addition, the robotic hand is also designed to prevent the silicon wafer from being thrown away even when the wafer is transported at high speed, and to prevent the silicon wafer itself from getting dirty.